Summary: “Software development is an ever-evolving industry. To succeed in it, you must keep an open eye for emerging opportunities and leverage them for your business success. Read further to learn what’s trending in software development industry right now.”
In the past two years, organizations have had to accelerate their digital transformation priorities, developing new business models and offerings to compete in an increasingly competitive marketplace. The shift in demand toward a personalized, dynamic online experience has created the demand for new digital products – all of this translated into software development, leading to the inception of new software development trends.
“IT executives see talent shortage as the most significant adoption barrier to 64% of emerging technologies.” – Gartner, 2021

We respect your privacy. Your information is safe.
Ongoing Software Development Trends for 2024 and Beyond
The future of software development looks bright for 2024, with the demand never higher for innovative products and solutions to meet the changing demands of the marketplace. In order to develop flexible, scalable solutions, pay attention to the following software development trends:
1. Low-Code / No-Code Platforms
Low-code development platforms (LCDP) and no-code development platforms (NCDP) offer pre-built blocks that can be dragged and dropped (visual environment) to assist in rapid development of mobile and web apps both by professional developers (for speed) and by those outside the IT department. While there are concerns over future flexibility, scalability, and security of software built using these low and no-code platforms, the platforms have lowered the bar to entry on software development, going mainstream in the last couple of years.
Gartner Forecasts Worldwide Low-Code Development Technologies Market to Grow 23% in 2021
Popular platforms for low-code/no-code development include Outsystems, Mendix, and Appian.
2. Machine Learning Operations
There has been a huge increase in demand for artificial intelligence (AI) and data science leveraging machine learning (ML) both inside and outside IT. This has an impact both on what is being developed and operated as well as how. Machine learning can be used in many stages of development, helping inform priorities and decisions, set accurate budgets, rapidly prototype, review and test, and even assist in programming.
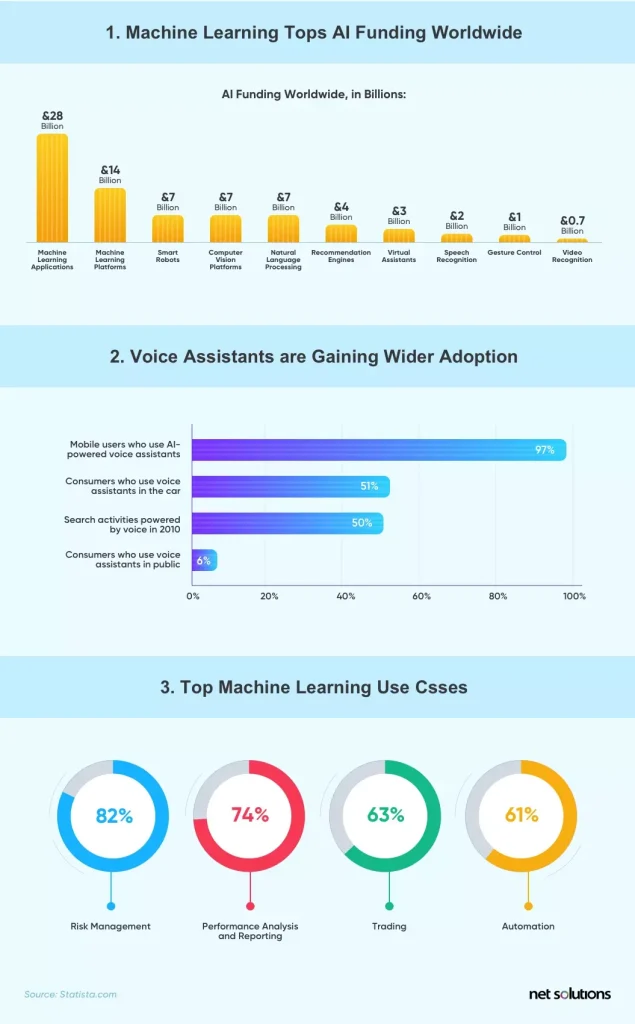
One of the machine learning methods making waves is Generative AI, the technology to create new content by using existing content (files, text, audio, images). Generative AI can be used to assist software development, in targeted marketing, and even assist in pharmaceutical development. It’s expected that within just 3 years, Generative AI will account for 10% of all data produced.
In software development, generative AI will be able to take over some of the more robotic elements of coding, more of an “augmented programming” assist, allowing programmers to work on higher-level coding requirements.
3. User Experience Design
User Experience Design (UXD or UED) is the process of enhancing user satisfaction of a software product by improving the usability, accessibility, and pleasure provided across each touch point. To do this, user experience design approaches every problem through the lens of the user to understand the user’s motivation, the actions taken to use the product, and how to seamlessly build and deploy the product to meet (or exceed) expectations. This UX design process begins and ends with the user
What are the 8 stages of the UX design process? Read on.
4. DevSecOps
DevSecOps (development, security, and operations) is an approach to software development (and culture) that embeds security throughout every stage of the DevOps pipeline.
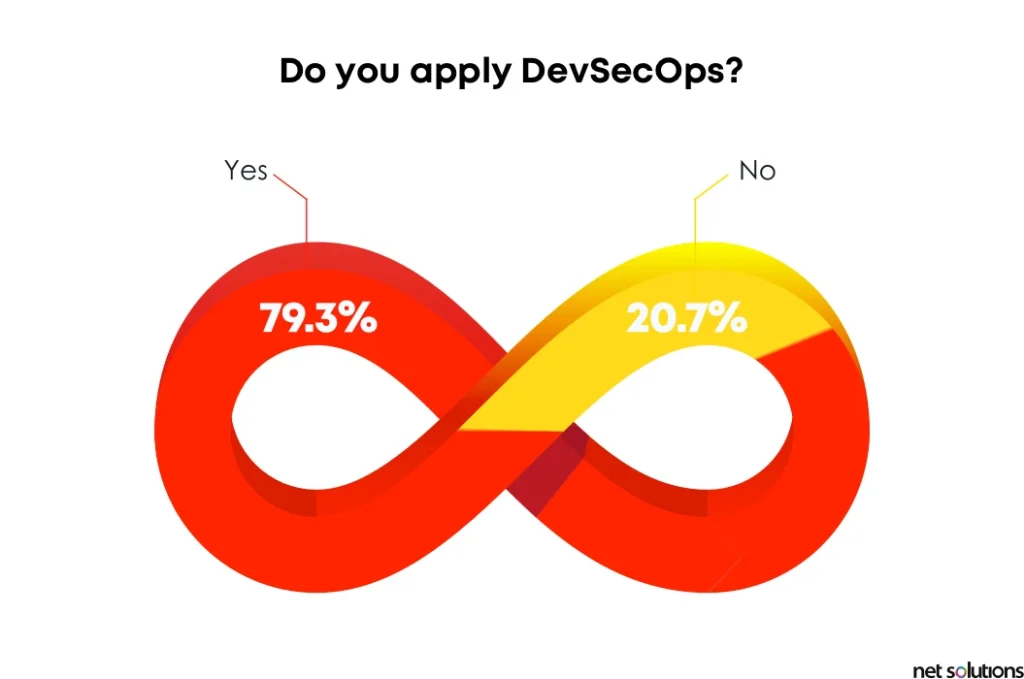
Security continues to be a top priority as organizations face growing threats and the highest cost for data breaches in recorded history (over $4.24 million on average). This creates pressure to ensure that software being used internally and by end users is secure by design. As a result, almost 80% of the surveyed organizations in our study have already begun applying DevSecOps in at least one of their teams to increase security and boost agility.
Similar to DevSecOps, the concept of shifting left in software development is the idea that security is embedded into each stage of development, instead of being left to the end of the development cycle. To shift left means that the code is designed to be secure, rather than made secure. Shifting left is both a mentality shift as well as the adoption of tools to detect security faults and vulnerabilities in the software, in dependencies, and in the runtime environment, database or APIs.
5. Omnichannel Experiences
Omnichannel experiences offer a seamless experience to the customer or user across various channels: retail, telephone, online, mobile, or social. For example, in eCommerce here’s what users expect:
- Seamless and frictionless access to information for quick reference and decision making across all touchpoints
- Anytime, anywhere access to data and operability (omnichannel retailing)
- Ability to shop or sell from any channel (including social platforms)
That’s why it is essential for service providers to ensure seamless touch points across sales, marketing, and customer service regardless of the device being used. Users will quickly jump ship if disrupted, fragmented omnichannel experience derails the core functionality of tasks across touchpoints.
However, omni channel experiences do not whip into shape out of thin air. A seamless integration of IoT, backend, and frontend is required to ensure successful omnichannel experiences. For this, software development teams must focus on interweaving individual silos among teams for delivering a superior customer experience.
Chick-Fil-A is a great example of how we can leverage the power of IoT and technology to offer a truly omnichannel experience. Their restaurants are busy and popular. But that’s not what makes them stand out. Their USP lies in their smart restaurants where they optimize the restaurant experience for owners and operators to ensure they can quickly serve tasty food with a personal touch.
For this, Chick-Fil-A has developed an Internet of Things platform where they gather insights and optimize their operations. Then, they use the gathered data to drive automation in their restaurants. As a result, customers get a personalized experience without having to stand in long queues. They also use the latest technologies to ensure that they’re always working and always on the top of their game.
6. The API Economy
The API economy is the use of APIs to achieve integration across services and data, allowing organizations to gain access to new services and products without building it themselves. The API economy is spinning off innovation across software development, including event-driven architecture, microservices, and omni-channel retailing.
7. Balanced Development Automation
Research from GitHub has demonstrated that automating software delivery alone can lead to a 31% faster merge and helps teams decrease time-to-market. Overall, the same research demonstrated that automation of repetitive tasks leads to a 27% improvement in team performance for open source and a 43% better at work.
8. Vulnerability Disclosure Programs
A vulnerability disclosure program (VDP) creates a secure channel for security issues and vulnerabilities to be reported following ISO standards around disclosure and handling and best practices around protecting whistleblowers. As more organizations and government agencies look toward cybersecurity preparedness, these programs are helping organizations become more proactive against threats.
9. Mobile First
Mobile traffic now makes up 54.8% of all web traffic, so it’s no longer about tagging a mobile website onto an existing design. Today, the approach needs to be mobile-first.
Rather than creating individual mobile websites that cater to various mobile and tablet platforms, screen sizes and resolutions, organizations are shifting to responsive web design to allow design elements to scale automatically.
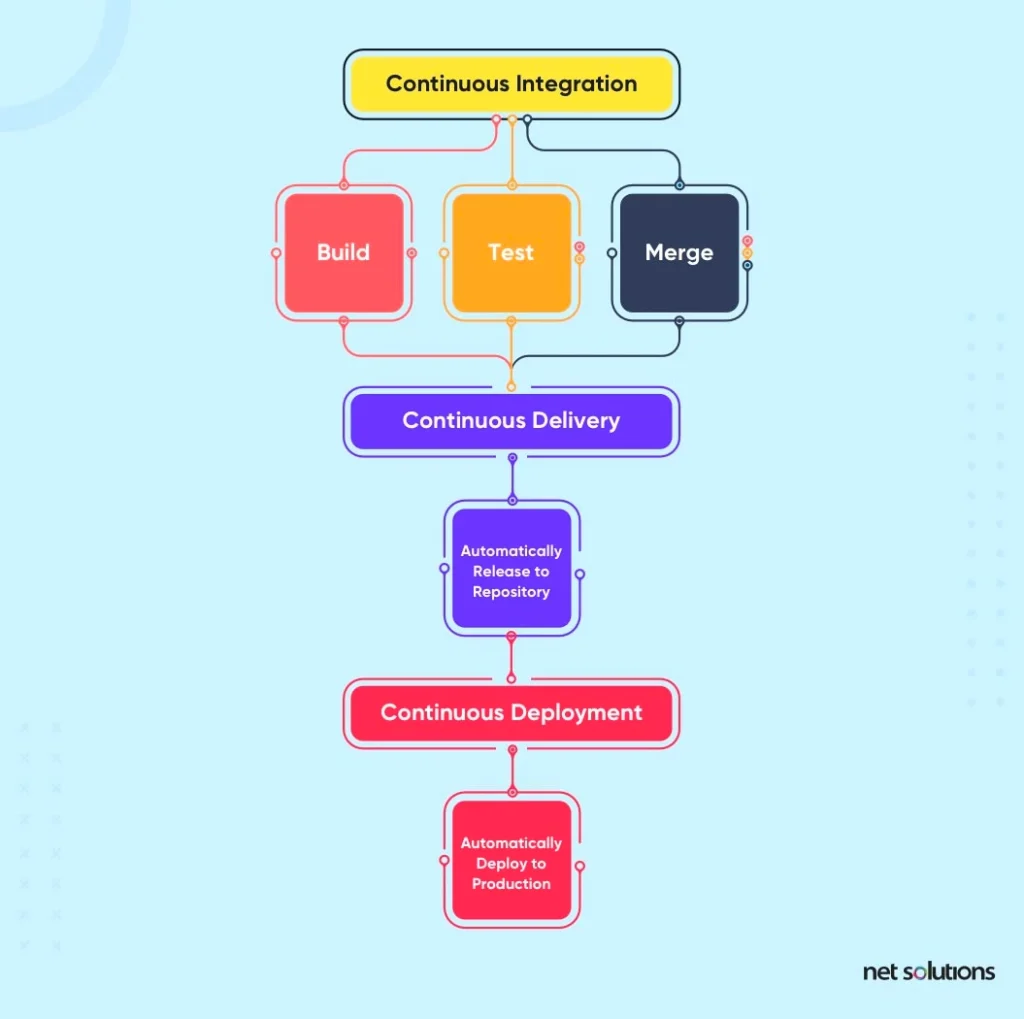
10. Continuous Integration and Delivery
Continuous integration, continuous delivery (CI/CD) is a way to introduce automation into the Agile and DevOps development process, a loop that implies constant updates to software to help improve quality and efficiency in the development process:
11. Serverless Computing
Serverless computing leverages managed cloud infrastructure (AWS, Azure, Google App Engine) to build apps without having to host or maintain the servers. As organizations look to focus on value-add activities, serverless computing holds a lot of appeal by offloading all the menial tasks around patching, scaling, or load balancing.
“Serverless architectures enable software developers to focus on what they should be doing — writing code and optimizing application design — making way for business agility.” – Gartner
12. Blockchain
Blockchain, the use of a decentralized network of computers for digital transactions, is one of rapidly growing software development trends, forecasted to reach $5,798 million by 2027 in healthcare alone. In healthcare, blockchain could be one of the tools to help identify inaccuracies in patient data, reduce breaches, and help support patient access to health records. Beyond just niche software products, blockchain-based decentralized applications (DApps) are being built to run on a blockchain (network) of computers instead of a single computer, allowing for greater flexibility and security, thanks to the use of smart contracts.
13. Expansion of the IoT
The Internet of Things (IoT) is expected to have a CAGR of 10.53% within the next 5 years, creating new platforms of “things” that can run software, but also changing how data is tracked and collected, how users engage across IoT devices (omnichannel expectations), and even impacting inventory management or shipping. All of this data must be translated into insight, with IoT spurring the need for AI and analytics.
Despite the promises of growth, the IoT market faces a chip shortage that will dampen the growth potential, which should resurge in the years moving forward.
14. Escalation of the Edge Computing
Edge computing, the concept of a distributed IT architecture, places service provisioning, data, and intelligence closer to devices and users to help boost performance. In essence, it helps bring the cloud closer to the user. Gartner predicts that Edge will work its way into every enterprise by 2025.
Moving into 2024, Edge is coming out of the hype cycle and is finding more solid footing with machine learning, analytics, and data aggregation. “Edge Computing is actually being implemented today in many of our clients’ environments, generating revenue, saving money, improving safety and customer experience, and enabling entirely new applications and data models,” notes Bob Gill for Gartner.
Edge will also be a part of innovative solutions to help businesses meet their goals around sustainability and reducing carbon footprints.
15. Quantum Computing
Quantum computing leverages quantum mechanics (superposition, interference, entanglement) to perform calculations, with the number of organizations and governments investing in quantum computing starting to improve processes and operations. While quantum computer (QC) hardware, software, and “as-a-service” options are still in their infancy, organizations should take note of this emerging technology to understand its future potential.
16. Big Data
Big data is a field that works with large or complex data sets of structured and unstructured data using advanced techniques. Big data is being influenced by the need to do better with unstructured data and to find a way to “tame” big data – ignoring what isn’t needed to find the “right” data from within. This is the needle in the haystack situation. Look toward concepts such as the data fabric (the flexible integration of data sources), understanding the options of the data marketplace, analytics, edge infrastructure, and AI.
17. Augmented Reality (AR)
Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) continue to find new avenues for growth, through gaming applications but also other use cases including eCommerce, healthcare, manufacturing, and education. Apple is also rumored to be releasing an AR/VR headset.
Brands should pay attention to the normalization of AR technologies. For example, as consumers become used to options such as real-time product preview or virtual try-on, augmented reality features will seem less futuristic and more a “norm” that is expected.
Conclusion
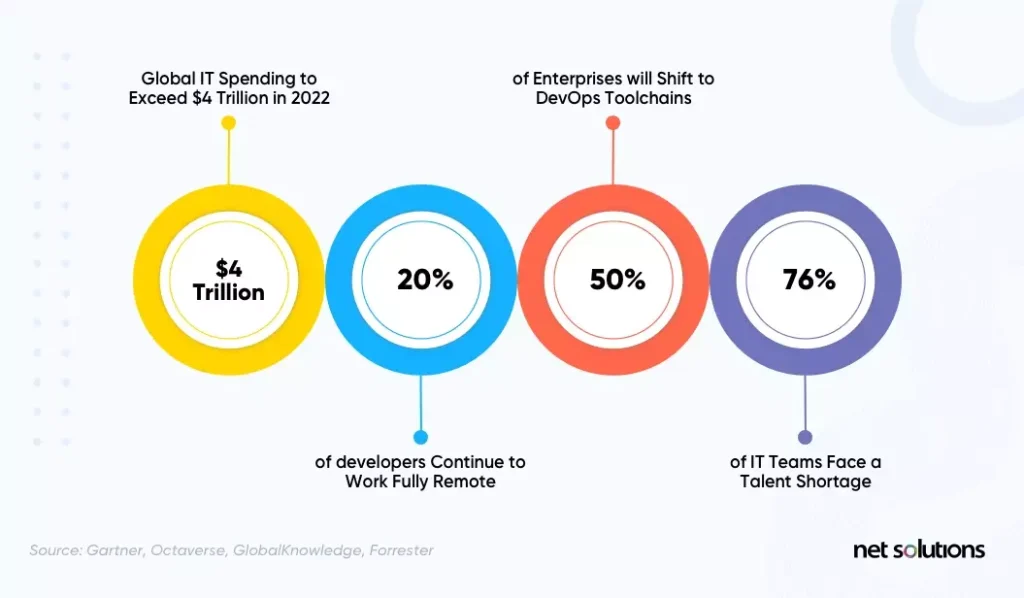
While most organizations are investing in emerging software development trends in 2024, talent shortage continues to remain the biggest obstacle to success, according to Gartner. “The ongoing push toward remote work and the acceleration of hiring plans in 2021 has exacerbated IT talent scarcity, especially for sourcing skills that enable cloud and edge, automation and continuous delivery,” said Yinuo Geng, research vice president at Gartner.
Don’t let a talent shortage get in the way of your plans to accelerate your digital transformation or transform your business with new products and services. Instead, rely on the trusted software development capabilities of Net Solutions. Recognized by Forrester and Gartner and trusted by leading startups and enterprises including Soaq, PayPal, Microsoft, and Dow Jones, we’re here to help you take advantage of all the latest software development trends to help position you for success in 2024 and beyond.





